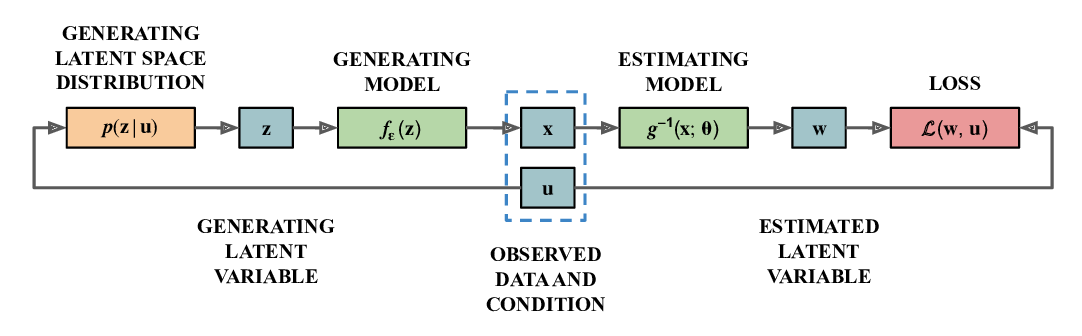
Abstract:
We design and conduct a simple experiment to study whether neural networks can perform several steps of approximate reasoning in a fixed dimensional latent space. The set of rewrites (i.e. transformations) that can be successfully performed on a statement represents essential semantic features of the statement. We can compress this information by embedding the formula in a vector space, such that the vector associated with a statement can be used to predict whether a statement can be rewritten by other theorems. Predicting the embedding of a formula generated by some rewrite rule is naturally viewed as approximate reasoning in the latent space. In order to measure the effectiveness of this reasoning, we perform approximate deduction sequences in the latent space and use the resulting embedding to inform the semantic features of the corresponding formal statement (which is obtained by performing the corresponding rewrite sequence using real formulas). Our experiments show that graph neural networks can make non-trivial predictions about the rewrite-success of statements, even when they propagate predicted latent representations for several steps. Since our corpus of mathematical formulas includes a wide variety of mathematical disciplines, this experiment is a strong indicator for the feasibility of deduction in latent space in general.