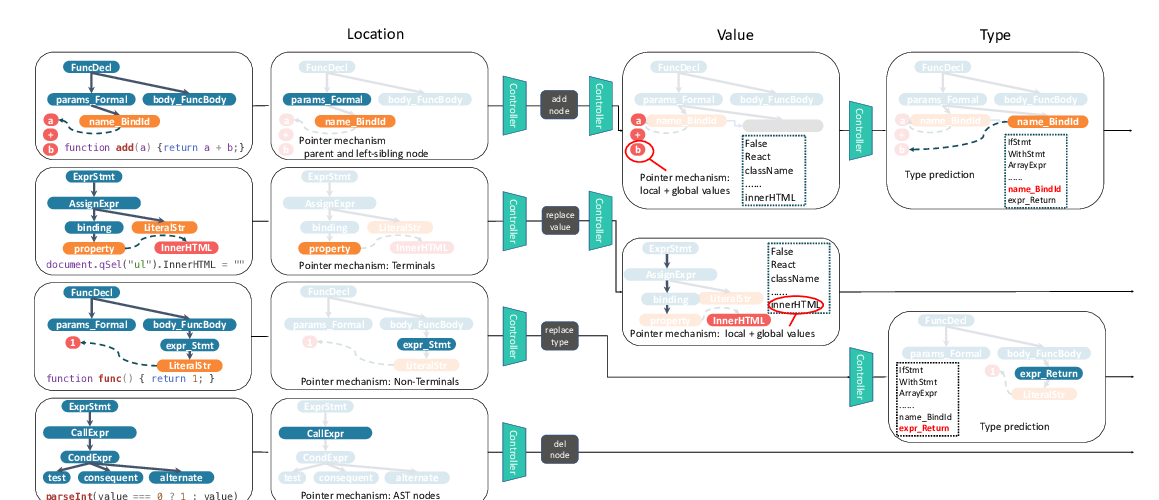
Abstract:
As gradual typing becomes increasingly popular in languages like Python and TypeScript, there is a growing need to infer type annotations automatically. While type annotations help with tasks like code completion and static error catching, these annotations cannot be fully inferred by compilers and are tedious to annotate by hand. This paper proposes a probabilistic type inference scheme for TypeScript based on a graph neural network. Our approach first uses lightweight source code analysis to generate a program abstraction called a type dependency graph, which links type variables with logical constraints as well as name and usage information. Given this program abstraction, we then use a graph neural network to propagate information between related type variables and eventually make type predictions. Our neural architecture can predict both standard types, like number or string, as well as user-defined types that have not been encountered during training. Our experimental results show that our approach outperforms prior work in this space by 14% (absolute) on library types, while having the ability to make type predictions that are out of scope for existing techniques.