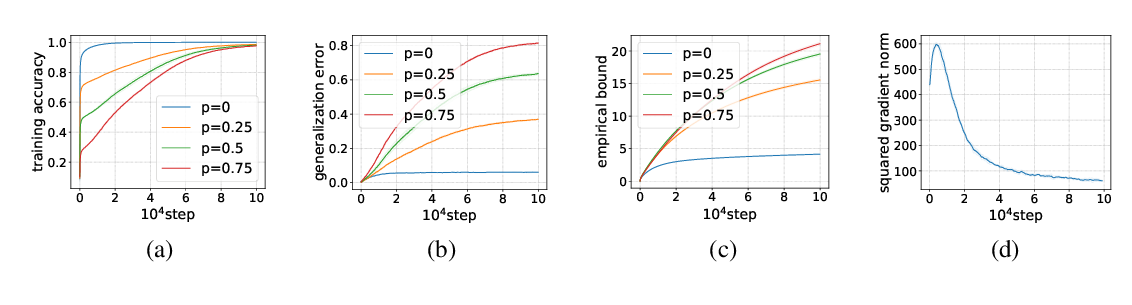
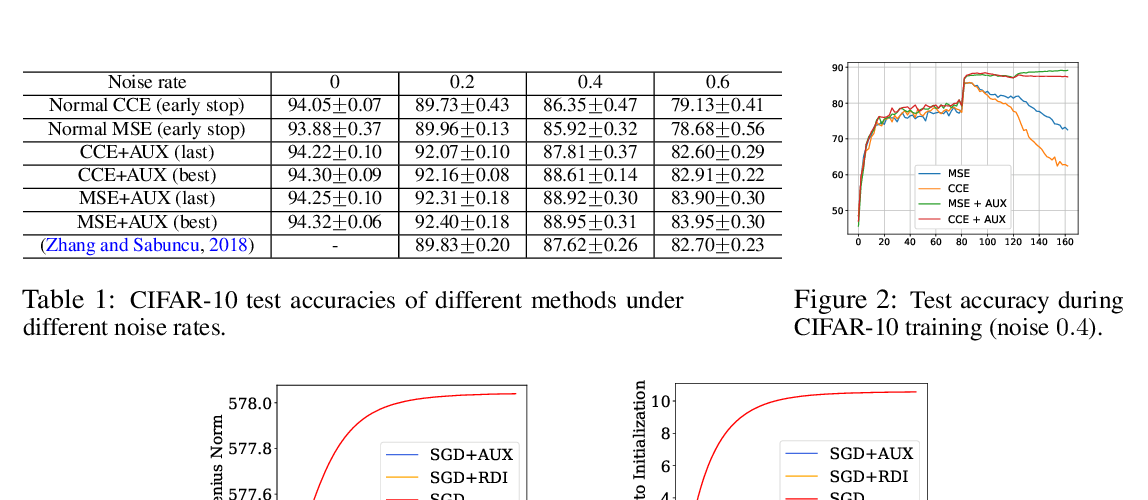
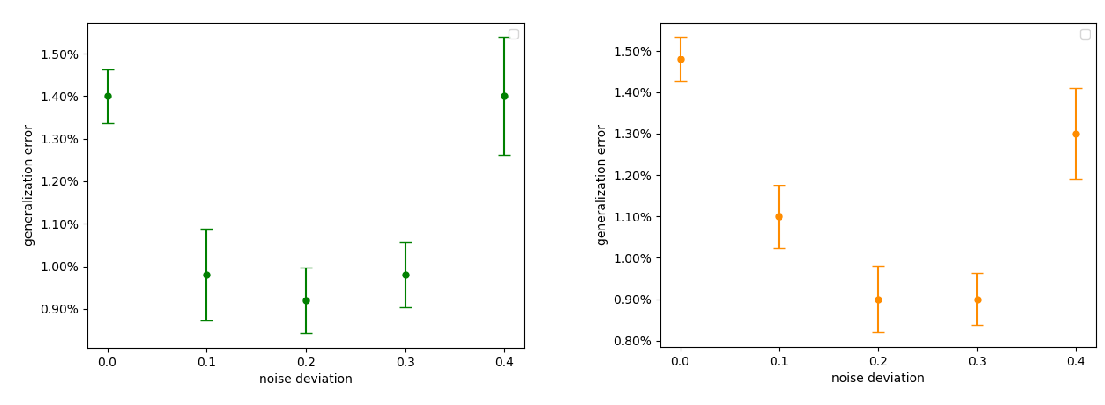
Abstract:
For linear classifiers, the relationship between (normalized) output margin and generalization is captured in a clear and simple bound – a large output margin implies good generalization. Unfortunately, for deep models, this relationship is less clear: existing analyses of the output margin give complicated bounds which sometimes depend exponentially on depth. In this work, we propose to instead analyze a new notion of margin, which we call the “all-layer margin.” Our analysis reveals that the all-layer margin has a clear and direct relationship with generalization for deep models. This enables the following concrete applications of the all-layer margin: 1) by analyzing the all-layer margin, we obtain tighter generalization bounds for neural nets which depend on Jacobian and hidden layer norms and remove the exponential dependency on depth 2) our neural net results easily translate to the adversarially robust setting, giving the first direct analysis of robust test error for deep networks, and 3) we present a theoretically inspired training algorithm for increasing the all-layer margin. Our algorithm improves both clean and adversarially robust test performance over strong baselines in practice.